Resolution
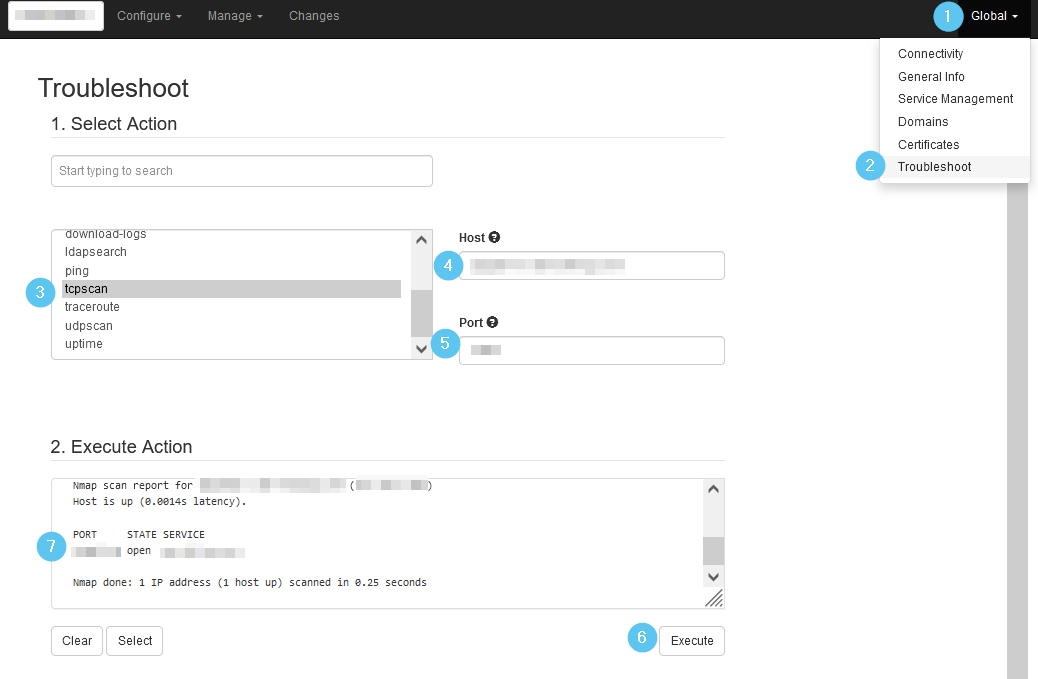
- Go to System Settings > Global > Troubleshoot.
- Select the tcpscan or udpscan action, depending on the type of communication which needs to be verified.
- Specify the host (IP or name) and port.
Hint: You can specify multiple ports. Separate them with a comma. - Hit [Execute] to see the output.
You'll see an "open" state if communication should be possible.
Mind that for UDP, you will also see an "open" state (e.g. port 53 for DNS, port 123 for NTP), but sometimes also an "open|filtered" state. Depending on the protocol, nmap may try a specific payload and correctly detect whether a port is open. In other cases, it may simply not receive a response. This implies that it's unsure whether the appliance can connect to this port or not.
If it only shows "filtered", it means there is a connectivity issue. Verify on your firewall if the appliance is allowed to connect to the specified host/port.
Common default ports when troubleshooting:
| 53 | DNS | UDP and TCP |
| 80 | http | TCP |
| 123 | NTP (Network Time Protocol) | UDP |
| 389 | LDAP | TCP |
| 443 | https | TCP |
| 636 | LDAPS | TCP |
| 1433 | Microsoft SQL Server | TCP |
| 3389 | RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) | UDP and TCP |
| 5432 | PostgreSQL | TCP |
Was this article helpful?
Tell us how we can improve it.