Description
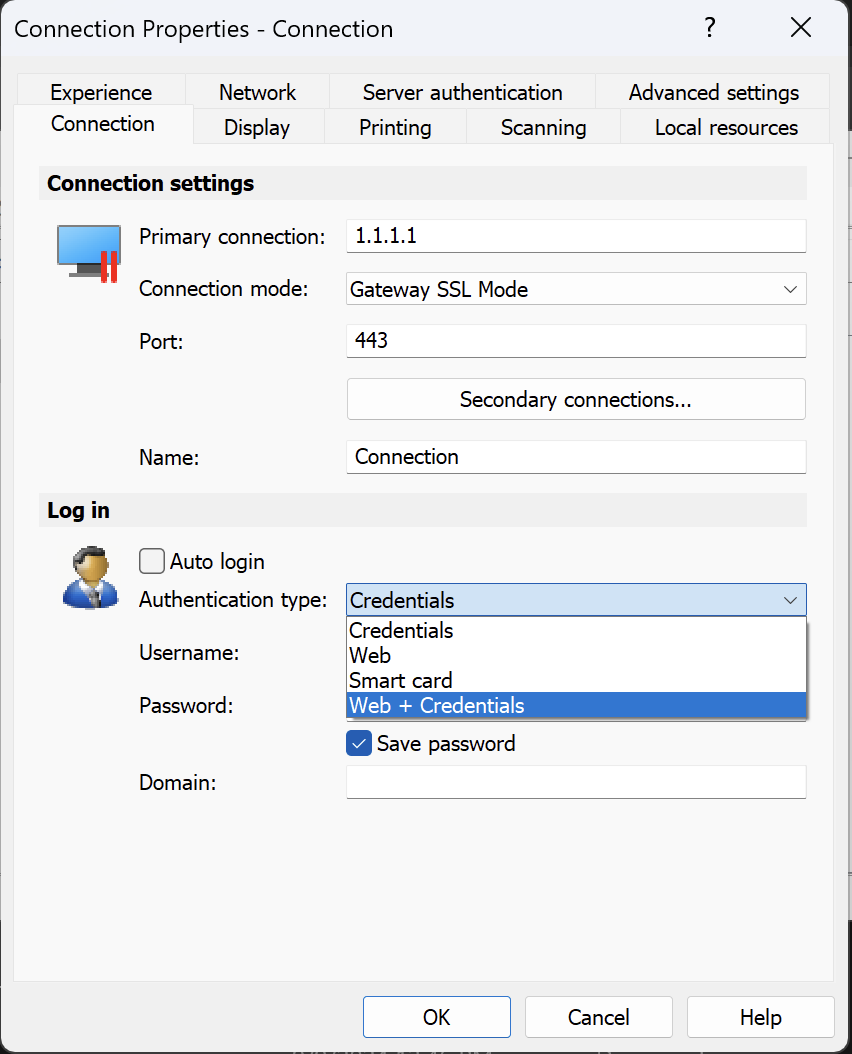
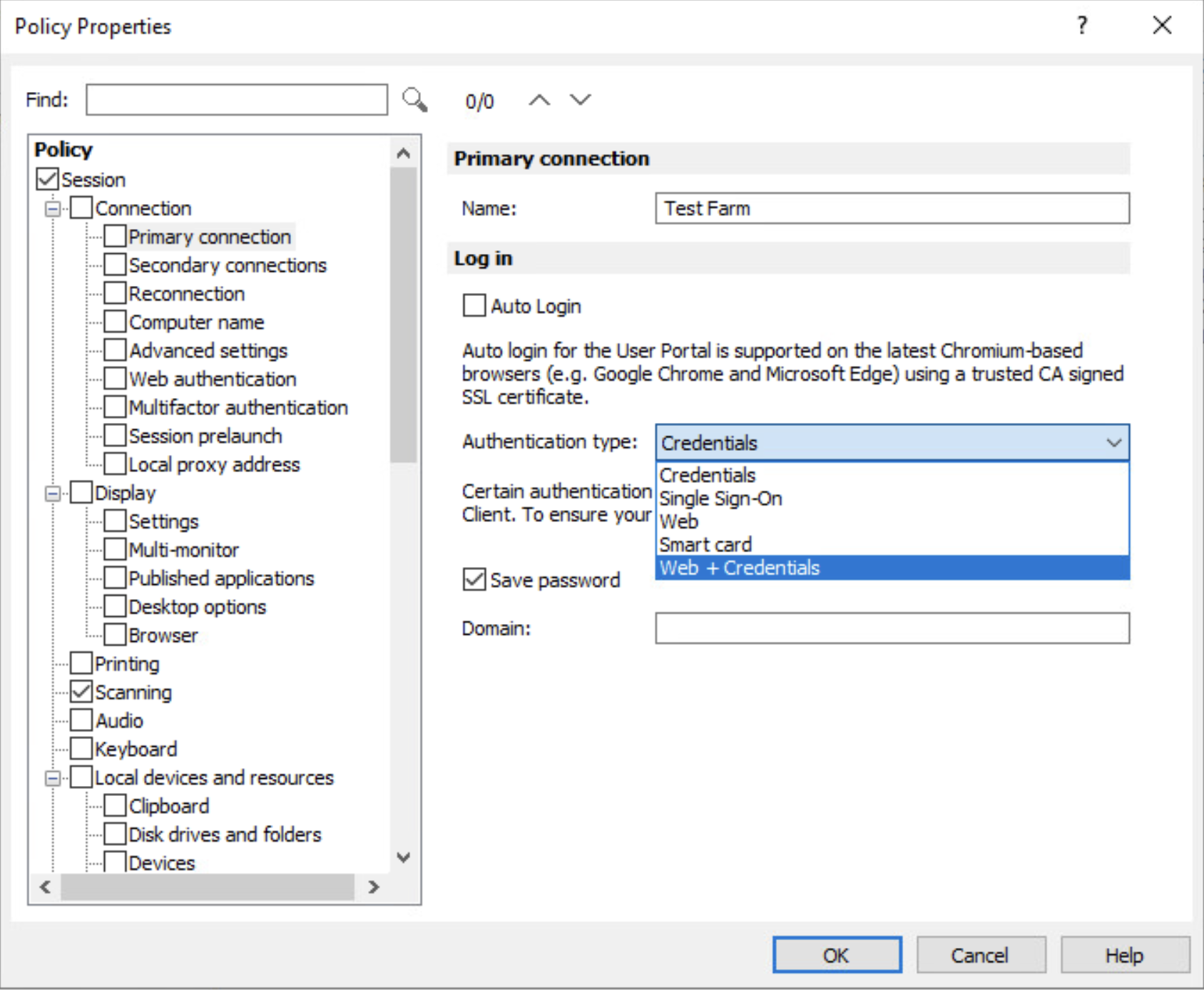
Parallels RAS allows the use of multiple authentication types with different clients. The available types are "Credentials", "Smart Card", "Web" (for SAML), and "Web + Credentials".
- Credentials. The user credentials are validated by the Windows system on which RAS is running. The credentials used for Windows authentication are also used to log in to an RDP session.
- Smart Card. Similar to Windows authentication, smart card credentials can be used with both RAS and RDP. Hence, smart card credentials only need to be entered once. Unlike Windows authentication, the user only needs to know the smart card’s PIN. The username is obtained automatically from the smart card, so the user doesn't need to provide it.
- Web (SAML). SAML SSO authentication is an XML-based authentication that provides single sign-on (SSO) capability between different organizations by allowing user authentication without sharing the local identity database.
- Web + Credentials. The same as Web (SAML), but users are prompted to enter credentials when they launch a published application. Authentication type "Web + Credentials" is used If you need to make use of SAML authentication without certificates. This type would still require the initial configuration of the IdP the same way as "Web", and a token would be retrieved based on the configured attribute mapped with the existing AD user. However, since certificates would not be used for identification, the end user would be prompted to enter credentials. For more information on how to enable the "Web + Credentials" authentication type, please refer to the following article.
You can see the authentication type used directly in the Parallels Client:
Authentication type can also be managed with a policy from Parallels RAS Console:
To check if the authentication type is available for your Parallels Client, please refer to the information below:
|
Parallels Client (platform) |
Credentials |
Smart Card |
Web (SAML) |
Web + Credentials |
|
Windows |
Y |
Y |
Y |
Y (19.4 and later) |
|
Web & PWA |
Y |
N |
Y |
Y (20.2 and later) |
|
macOS |
Y |
Y |
Y |
N |
|
Linux |
Y |
N |
Y |
N |
|
Android |
Y |
N |
Y |
N |
|
iOS/iPadOS |
Y |
N |
Y |
N |
Was this article helpful?
Tell us how we can improve it.