The Device Manager feature allows the administrator to convert Windows devices running Windows 8 up to Windows 11 into a Thin-Client-like OS. To do this, the administrator must first choose to manage devices connecting to the farm. In order to be managed, Windows devices must be running a current version of the Parallels Client for Windows.
Below are the procedures required to connect the Parallels Client for Windows to a farm and further enroll and manage the device.
Install and Configure
First, download the Parallels Client for Windows and double-click to run the RDPClient.msi or RDPClientx64.msi and proceed through the installation wizard (install the 64-bit version on 64-bit Windows).
Upon completion, run the Parallels Client and configure a new Parallels Remote Application Server connection according to the steps below:
-
Click File.
-
Click Add New Connection.
-
Select Parallels Remote Application Server and click OK.
- Next, configure the connection properties below:
- Primary Connection - Specify the Parallels Remote Application Server FQDN or IP
- User Credentials - Enter Username, password, and domain
- Click OK to create the new connection.
Upon completion, the Windows device will appear in the Devices list shown from the Device Manager category and have access to published resources.
Windows Device Enrollment
Features such as Power Off, Reboot, and Shadow require that the Windows device is managed. Windows devices can be set to automatically be managed by your farm or require that the admin approves them first.
Approve a device to be managed by Parallels Remote Application Server from the Parallels RAS Console according to the following steps:
- Go to Device Manager > Devices.
- Select a device.
- Click Tasks.
- Click Manage Device.

The device state will change to Pair Pending until the device reconnects. Ensure the Client Manager Port is enabled from Farm > Gateways > Select gateway > Tasks > Properties > Network. If disabled, the device will remain in a Pair Pending state.
Once the Parallels Client reconnects, the enrollment process is complete and the device state is updated to Logged On, which indicates that it is managed by Parallels Remote Application Server.
Alternatively, set Parallels Remote Application Server to automatically manage Windows devices according to the next steps:
- Go to Device Manager.
- Click Options.
- Enable Automatically Manage Windows Devices.
The administrator can now check the state of the device and perform power control actions such as Power On, Power Off, Reboot, and Logoff.
Note: Devices running outdated versions of the Parallels Client cannot be managed and are marked as Not Supported.
Shadow a Windows Device
Shadow a Windows device to gain access to the full desktop and control applications running locally on the system as well as any remote applications published from Parallels Remote Application Server.
Shadow a Windows device according to the following steps:
- Go to Device Manager > Devices.
- Select a device.
-
Click Shadow.
Note: The Windows user will be prompted to allow the administrator to take control and can choose to deny access. The Request Authorization prompt can be deactivated by the administrator from Client Manager > Devices > Select Windows device > Tasks> Properties > Shadowing.
In addition, shadowing requires a direct connection between the machine from where the console is running and the device itself.
Desktop Replacement
The Replace desktop option limits users from changing system settings or installing new applications. Replace the Windows Desktop with the Parallels Client, to convert the Windows operating system into a thin-client-like OS without replacing the operating system. This way, the user can only deploy applications from the Parallels Client, providing the administrator with a higher level of control over connected devices. Additionally, Kiosk Mode limits the user from power cycling only when enabled.
To enable the Replace desktop feature:
- Select a Windows device and click Tasks.
- Click Properties.
- Click OS Settings.
- Enable Replace Desktop.
-
Click OK.
Note: This feature requires an administrative password set to switch between user and admin mode on the Windows device. If Use Group Settings is enabled, settings are inherited from the group that the device belongs to.
Switching to Admin Mode
In user mode, the user is restricted to using only the applications provided by the administrator. In order to change system settings, switch the device to administration mode.
Change to admin mode by right-clicking on the system tray icon, selecting Switch to admin mode, and providing the password configured.
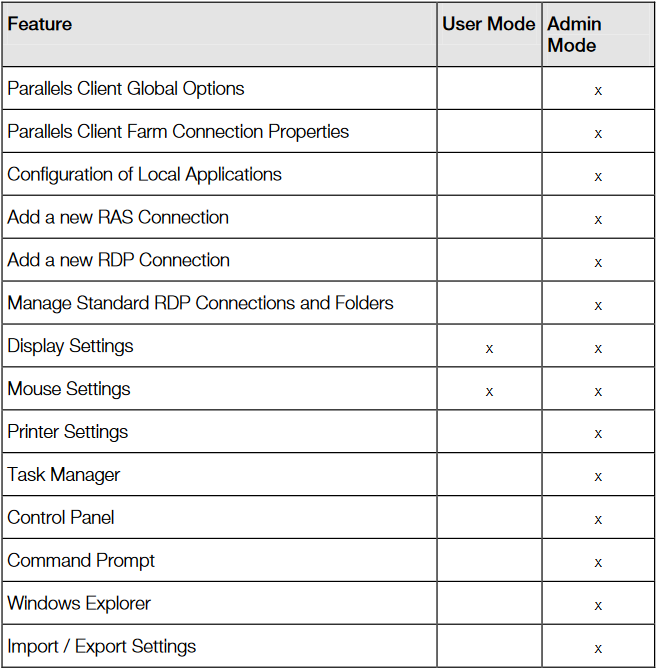
The table above outlines features available in admin mode and user mode.
Configuring Local Applications when using the Parallels Client Desktop Replacement
With the Replace Desktop option enabled, the administrator’s target should be to deploy remote applications or remote desktops and use the native OS simply to deploy the software needed to connect remotely. However, in some instances local applications may be needed. The administrator still has the ability to configure local applications to be shown within the Parallels Client Desktop Replacement, however it is necessary to switch to admin mode first.
Publish a local application according to the following steps:
- Shadow the user’s session or use the user device station directly.
- Switch the Parallels Client Desktop Replacement to admin mode.
- Click File > Add New Application.
- Fill in the application information.
- Applications added will be visible in the Application Launcher.
- Switch back to user mode once all the applications needed are configured.
Was this article helpful?
Tell us how we can improve it.